
Product: Abaqus/Standard
Abaqus/Standard offers a “direct” steady-state dynamic analysis procedure for structures subjected to continuous harmonic excitation.
Abaqus/Standard also offers a “modal” procedure described in “Steady-state linear dynamic analysis,” Section 2.5.7 and a“subspace” procedure described in “Subspace-based steady-state dynamic analysis,” Section 2.6.2.
The direct” steady-state dynamic analysis procedure is a perturbation procedure, where the perturbed solution is obtained by linearization about the current base state. For the calculation of the base state the structure may exhibit material and geometrical nonlinear behavior as well as contact nonlinearities. Structural and viscous damping can be included in the procedure using the Rayleigh and structural damping coefficients specified under the material definition. Discrete damping such as mass, dashpot, spring, and connector elements can be included. In addition, global damping coefficients ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() can be specified at the procedure level to define additional viscous and structural damping contributions. The procedure can also be used for coupled acoustic-structural medium analysis (“Coupled acoustic-structural medium analysis,” Section 2.9.1), piezoelectric medium analysis (“Piezoelectric analysis,” Section 2.10.1), and viscoelastic material modeling (“Frequency domain viscoelasticity,” Section 4.8.3). All properties can be frequency dependent.
can be specified at the procedure level to define additional viscous and structural damping contributions. The procedure can also be used for coupled acoustic-structural medium analysis (“Coupled acoustic-structural medium analysis,” Section 2.9.1), piezoelectric medium analysis (“Piezoelectric analysis,” Section 2.10.1), and viscoelastic material modeling (“Frequency domain viscoelasticity,” Section 4.8.3). All properties can be frequency dependent.
The formulation is based on the dynamic virtual work equation,
whereFor the steady-state harmonic response we assume that the structure undergoes small harmonic vibrations about a deformed, stressed state, defined by the subscript 0. Since steady-state dynamics is a perturbation procedure, the load and response in the step define the change from the base state. The change in internal force vector follows by linearization:
![]()
![]()
![]()
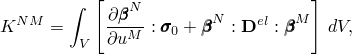
![]()
![]()
For harmonic excitation and response we can write
![]()
![]()
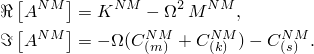
The procedure is activated by defining a direct-solution steady-state dynamic analysis step. Both real and imaginary loads can be defined.
As output Abaqus/Standard provides amplitudes and phases for all element and nodal variables at the requested frequencies. For this procedure all amplitude references must be given in the frequency domain.