| Abaqus Keywords Reference Guide |
|
| How to find keyword examples |

This option is used to define cavity symmetry by periodic repetition in a given direction. It can be used only following the *RADIATION SYMMETRY option.
Products: Abaqus/Standard Abaqus/CAE
Type: History data
Level: Step
Abaqus/CAE: Interaction module
Set TYPE=2D to create a cavity composed of the cavity surface defined in the model and a series of similar images generated by its repetition according to a two-dimensional distance vector. The repeated images are bounded by lines parallel to line ![]() (see Figure 16.10–1). The distance vector must be defined so that it points away from line
(see Figure 16.10–1). The distance vector must be defined so that it points away from line ![]() and into the domain of the model. This option can be used only for two-dimensional cases.
and into the domain of the model. This option can be used only for two-dimensional cases.
Set TYPE=3D to create a cavity composed of the cavity surface defined in the model and a series of similar images generated by its repetition according to a three-dimensional distance vector. The repeated images are bounded by planes parallel to plane ![]() (see Figure 16.10–2). The distance vector must be defined so that it points away from plane
(see Figure 16.10–2). The distance vector must be defined so that it points away from plane ![]() and into the domain of the model. This option can be used only for three-dimensional cases.
and into the domain of the model. This option can be used only for three-dimensional cases.
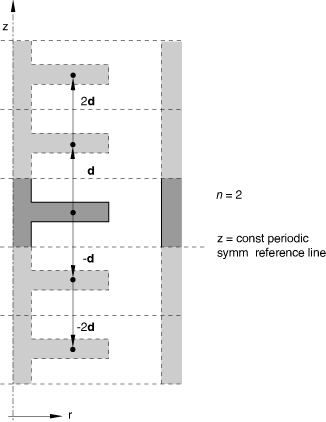
Set TYPE=ZDIR to create a cavity composed of the cavity surface defined in the model and a series of similar images generated by its repetition in the z-direction. The repeated images are bounded by lines of constant z-coordinate (see Figure 16.10–3). The z-distance vector must be defined so that it points away from the z-constant periodic symmetry reference line and into the domain of the model. This option can be used only for axisymmetric cases.
Set this parameter equal to the number of repetitions used in the numerical calculation of the cavity view factors resulting from the periodic symmetry. The result of this symmetry is a cavity composed of the cavity surface defined in the model plus twice NR similar images, since the periodic symmetry is assumed to apply both in the positive and negative directions of the distance vector. The default value is NR=2.
First (and only) line:
x-coordinate of point a (see Figure 16.10–1).
y-coordinate of point a.
x-coordinate of point b.
y-coordinate of point b.
x-component of periodic distance vector.
y-component of periodic distance vector.
First line:
x-coordinate of point a (see Figure 16.10–2).
y-coordinate of point a.
z-coordinate of point a.
x-coordinate of point b.
y-coordinate of point b.
z-coordinate of point b.
Second line:
x-coordinate of point c.
y-coordinate of point c.
z-coordinate of point c.
x-component of periodic distance vector.
y-component of periodic distance vector.
z-component of periodic distance vector.
First (and only) line:
z-coordinate of periodic symmetry reference line (see Figure 16.10–3).
z-component of periodic distance vector.
Figure 16.10–1 *PERIODIC, TYPE=2D option.

Figure 16.10–2 *PERIODIC, TYPE=3D option.
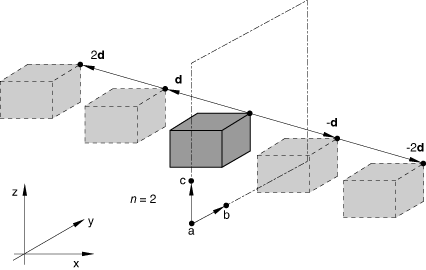
Figure 16.10–3 *PERIODIC, TYPE=ZDIR option.